When mounted to the underside of a piece of equipment, casters and wheels make it easier for personnel or machinery to transport a load or group of items from one place to another in a manufacturing or distribution facility. Typical industrial applications include platform trucks, carts, hand trucks, assemblies and tow line conveyor carriers.
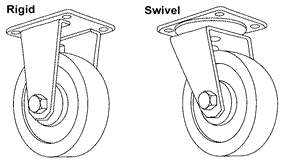
There are several types of casters and wheels. These include:
The appropriate choice of caster wheels depends on many application-specific factors, such as:
Here are examples of 3 types of bearings used in the manufacturing on quality casters and wheels:

Manufacturers provide many accessories for specific applications:
The user is responsible for proper maintenance and operation of equipment. Some equipment is abused or subjected to unreasonable demands. Don't overload or drop loads on carts or trucks. High speeds on rough floors can create severe impact or shock loads that may cause wheel or equipment failure. Periodically examine equipment for:
Casters and wheels are used in a variety of areas to support processing and picking throughout a facility:
Casters and wheels provide a variety of benefits:
Casters and wheels are used in nearly every industry, including:
Copyright MHI © 2023 | All Rights Reserved